Gate valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow of liquids and gases within pipelines. As one of the most widely used types of valves, gate valves are essential components in various industries, including water treatment, oil and gas, and manufacturing. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the purpose, design, and applications of gate valves. Moreover, we will provide practical advice on how to choose the right gate valve for your needs, ensuring efficiency, durability, and safety. This article will also cover the different types of gate valves and how to properly maintain them, helping you make an informed decision.
What Are Gate Valves?
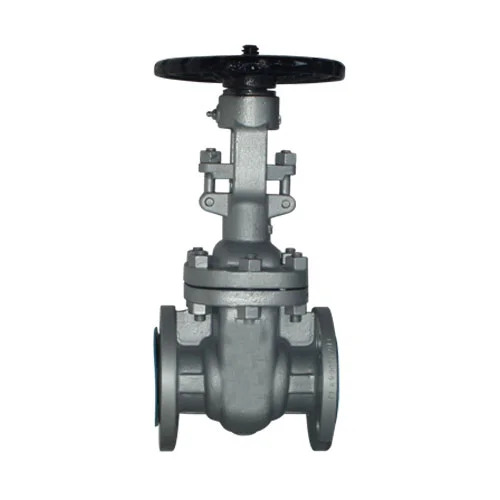
Gate valves are mechanical devices used to start or stop the flow of fluids in pipelines. They operate by lifting a gate or wedge out of the path of the flow, allowing the fluid to pass freely through. When closed, the gate valve forms a tight seal, preventing any leakage. Gate valves are typically used in applications where the flow needs to be fully shut off or allowed to pass with minimal resistance.
How Do Gate Valves Work?
Gate valves operate by utilizing a wedge-shaped gate that is moved up and down using a stem. When the valve is open, the gate is raised, allowing fluids to flow through the pipeline. When the valve is closed, the gate is lowered, sealing off the flow path. Gate valves are classified into two main categories: parallel slide gate valves and wedge gate valves. The design and construction of these valves make them suitable for handling high-pressure systems and large volumes of liquid or gas.
Gate Valve Applications
Gate valves are used in a wide range of applications across various industries. They are most commonly found in water treatment plants, wastewater systems, oil and gas pipelines, power generation, and chemical processing facilities. Gate valves are particularly useful when a full-flow, on/off control is needed without restricting the flow. They are not ideal for regulating the flow of fluids, as their design does not allow for precise control of the flow rate.
Different Types of Gate Valves
Gate valves come in different types, each designed for specific applications and fluid types. Below are the main types of gate valves you may encounter:
1. Wedge Gate Valves
Wedge gate valves are the most common type of gate valve used in industrial applications. They feature a wedge-shaped gate that moves up and down to regulate the flow. The wedge gate is typically made from durable materials like stainless steel or cast iron, making it suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments. Wedge gate valves are often used in pipelines for oil and gas, water distribution, and chemical processes.
2. Parallel Slide Gate Valves
Parallel slide gate valves differ from wedge gate valves in their design. They use a pair of parallel gates that slide in and out of the flow path. These valves are typically used in low-pressure applications where precise control of the flow is not required. They are often seen in water and sewage treatment plants.
3. Resilient-Seated Gate Valves
Resilient-seated gate valves use a flexible elastomer seat to form a tight seal when the valve is closed. The elastomer seat allows for better sealing performance in low-pressure systems and prevents leakage when the valve is not in use. These valves are commonly used in water distribution systems and sewage treatment plants.
4. Knife Gate Valves
Knife gate valves are specifically designed for slurry and wastewater applications, where the fluid contains solids. They feature a sharp, knife-like gate that can cut through solid particles, ensuring that the valve maintains its ability to seal tightly even in the presence of solids. Knife gate valves are used in industries such as mining, paper manufacturing, and wastewater treatment.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Gate Valves
Choosing the right gate valve for your application requires careful consideration of several key factors. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision.
1. Pressure and Temperature Requirements
Gate valves are designed to handle specific pressure and temperature conditions. Before selecting a gate valve, it’s crucial to assess the pressure and temperature ranges of your pipeline system. You need a valve that can withstand the maximum pressure and temperature that your system will experience. Be sure to check the valve's pressure rating, which is typically indicated by the manufacturer.
2. Material Selection
The material of the gate valve plays a significant role in its performance and durability. The most common materials used in gate valves include stainless steel, cast iron, bronze, and carbon steel. Each material has its own advantages and is suitable for different types of fluids and operating environments. For instance, stainless steel gate valves are ideal for corrosive fluids, while cast iron valves are more suitable for water and non-corrosive fluids.
3. Valve Size
Gate valves come in various sizes to accommodate different pipeline diameters. Selecting the correct size ensures that the valve functions properly and provides a good seal. You’ll need to consider the size of your pipeline when selecting a gate valve. The valve should fit snugly in the pipeline to prevent any leakage.
4. Valve End Connections
Gate valves are available with different types of end connections, including flanged, threaded, and welded connections. The type of connection you choose depends on the configuration of your pipeline and how the valve will be installed. Flanged connections are the most common, especially in large industrial applications.
5. Actuation Type
Gate valves can be operated manually, automatically, or remotely, depending on your needs. Manual operation involves using a handwheel or lever to open and close the valve. Automated systems use electric or pneumatic actuators to operate the valve, while remote operation allows for the control of the valve from a distance. Consider the operating conditions and automation needs of your system when selecting a gate valve.
6. Sealing Performance
The sealing performance of a gate valve is essential for ensuring that the valve functions properly without leakage. Check the sealing design of the gate valve to ensure it provides a tight seal when closed. Some gate valves use resilient materials like rubber or elastomer to improve sealing performance, especially in low-pressure systems.
How to Maintain Gate Valves for Optimal Performance
Proper maintenance of gate valves is essential to ensure they continue to perform effectively over time. Here are some tips for maintaining gate valves:
1. Regular Inspection
Perform regular inspections of your gate valves to ensure they are in good working condition. Look for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage to the valve components. Check the valve's sealing surfaces to make sure they are not worn down or damaged.
2. Lubrication
Lubricating the stem and other moving parts of the gate valve can prevent wear and ensure smooth operation. Use the recommended lubricant for the specific type of gate valve you have, and apply it periodically to reduce friction and prolong the valve's lifespan.
3. Cleaning
Gate valves should be cleaned regularly to remove dirt, debris, or buildup that may affect their performance. Clean the valve's external parts as well as the internal components to ensure proper operation. For valves used in wastewater or slurry systems, cleaning becomes especially important to maintain the valve's sealing ability.
4. Tightening and Sealing
Ensure that all bolts and seals are properly tightened during maintenance. Loose connections or worn seals can cause leaks or prevent the valve from sealing properly. Regularly check for any signs of leakage around the valve body and replace any damaged seals.
Frequently Asked Questions About Gate Valves
1. What is the difference between gate valves and ball valves?
The primary difference between gate valves and ball valves lies in their design and functionality. Gate valves are used for fully opening or closing the flow, while ball valves are more commonly used for controlling the flow rate. Gate valves provide less resistance to flow, making them ideal for on/off applications, whereas ball valves are better suited for regulating flow.
2. Can gate valves be used in high-pressure systems?
Yes, gate valves are suitable for high-pressure systems, especially wedge gate valves. These valves are designed to handle high pressure and temperature conditions, making them ideal for use in industries such as oil and gas, power generation, and chemical processing.
3. Are gate valves suitable for regulating flow?
Gate valves are not recommended for regulating flow. Their design is more suited for full-flow, on/off control. For applications requiring precise flow regulation, control valves such as ball valves or globe valves are better choices.
4. How do I choose the right gate valve material?
The choice of material for your gate valve depends on the type of fluid, pressure, and temperature conditions of your system. Stainless steel is ideal for corrosive fluids, while cast iron is better suited for water and non-corrosive applications. Always consult with a valve supplier to ensure you choose the best material for your specific needs.
Conclusion: Selecting the Best Gate Valve
Gate valves are essential components in many industries, offering reliable on/off flow control in pipelines. By understanding the different types of gate valves, their applications, and the factors to consider when selecting one, you can ensure optimal performance and safety in your pipeline system. Regular maintenance and proper installation will further extend the lifespan of your gate valves, providing long-term value for your operations.
Make sure to carefully evaluate the pressure, temperature, material, and size requirements of your system before selecting a gate valve. With the right valve in place, you can maximize efficiency, minimize downtime, and ensure smooth operations across your pipeline network.